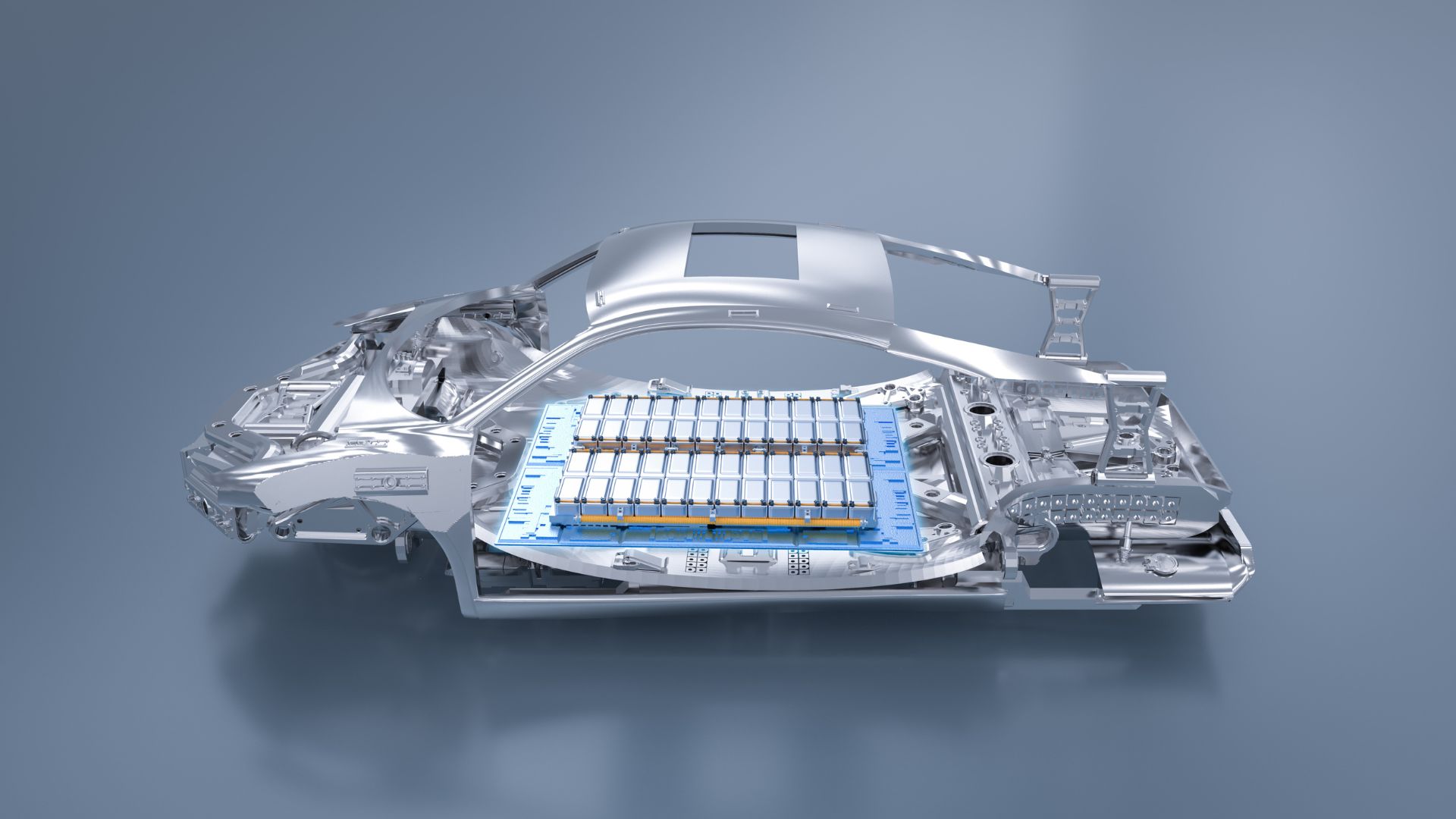
Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming increasingly popular as the world transitions towards sustainable transportation solutions. At the heart of every electric vehicle lies its battery pack, a crucial component that powers the vehicle’s electric motor. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at electric vehicle batteries, demystifying their technical aspects in simple terms.
Understanding Electric Vehicle Batteries
Electric vehicle batteries are rechargeable energy storage devices that provide the necessary power to propel the vehicle. Unlike traditional internal combustion engine vehicles that rely on gasoline or diesel, electric vehicles harness the energy stored in their batteries to drive an electric motor.
Composition and Structure
Electric vehicle batteries are typically made up of lithium-ion cells. These cells consist of several layers, including electrodes, separators, and electrolytes. The electrodes, usually made of lithium compounds, store and release electrical energy during charging and discharging cycles. The separator prevents the electrodes from coming into direct contact, ensuring the safe operation of the battery. The electrolyte facilitates the movement of lithium ions between the electrodes during charging and discharging.
Battery Management System (BMS)
To ensure the optimal performance and longevity of electric vehicle batteries, they are equipped with a sophisticated Battery Management System (BMS). The BMS monitors various parameters such as temperature, voltage, and state of charge to manage the charging and discharging processes effectively. It also helps prevent overcharging, over-discharging, and overheating, which can damage the battery and affect its performance.
Range and Energy Density
One of the critical factors determining the practicality of electric vehicles is their range, i.e., how far they can travel on a single charge. Range is closely related to the energy density of the battery, which refers to the amount of energy stored per unit volume or weight of the battery pack. Advances in battery technology have led to improvements in energy density, allowing electric vehicles to achieve longer ranges on a single charge.
Charging Infrastructure
The charging infrastructure plays a vital role in the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. Different types of charging stations, such as Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast chargers, offer varying charging speeds and compatibility with different electric vehicle models. The availability of charging stations and the charging time required also influence the convenience and practicality of electric vehicle ownership.
Environmental Impact
Electric vehicles are often touted as environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional vehicles due to their zero tailpipe emissions. However, it’s essential to consider the environmental impact of electric vehicle batteries throughout their lifecycle, including raw material extraction, manufacturing, use, and end-of-life disposal or recycling. Efforts are underway to develop more sustainable battery chemistries and recycling technologies to minimize environmental footprint.
Conclusion
Electric vehicle batteries are at the forefront of the transition towards sustainable transportation. Understanding the technical aspects of electric vehicle batteries, including their composition, structure, management, range, charging infrastructure, and environmental impact, is essential for both consumers and policymakers. As battery technology continues to evolve, electric vehicles are poised to play a significant role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the impacts of climate change.